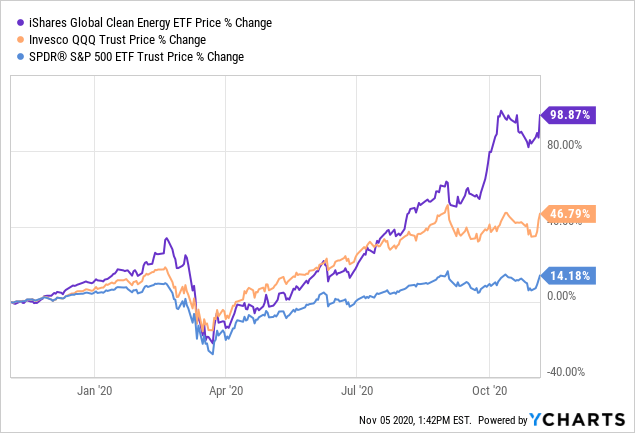
Knowing peak demand is key to planning for reliable power systems. Peak demand dictates how much power system capacity is needed to meet reliability standards. Although peak demand is expected decrease slightly each year it is an important element in system planning. By 2028, peak demand is projected to decrease by 0.14% annually.
ICAP
ICAP is a pricing mechanism that provides utilities with signals to encourage investment and ensure resource adequacy. Utilities typically purchase ICAP power plants in New York to meet excess wholesale tariff requirements and peak load requirements. These are approved by federal regulators. ICAP is used for mandatory capacity markets such ISO New England, PJM Interconnection. It is also used by Texas and other states.
IRM
IRM is an element of reliability rules that the New York electricity grid must follow. It is the calculation of the supply resources available to meet peak demand. It is based upon the most recent load models. It also considers demand response and energy storage technologies. These enable the lights to remain on during an outage.

DERs
Distributed energy resources (DERs), which vary production and consumption, provide power quality value. This can help reduce energy losses as well as prevent voltage excursions at distribution feeders. In addition, DERs are able to provide additional capacity to power plants when demand fluctuates.
Generator deactivation assessment
To reduce ozone levels, NYISO has instituted stricter regulation of simple-cycle combustion turbine plants. Owners of power plants must comply with the new rules by 2023 or 2025. Current New York's peak power generation capacity of 648MW is being phased down. A total of 1,300MW of peak capacity are being retrofitted. New York's peak power generation capacity also has higher average temperatures compared to the rest of America. As a result, these plants' deactivation can lead to higher-than-normal demand.
DER participation model
The DER participation model in NYISO is designed to ensure that DERs are connected to a transmission node that is capable of responding to dispatch instructions. This is a requirement in order to protect the reliability of New York power plants. The DERs must meet specific criteria that meet the standards of the New York state Reliability Committee. These requirements include inverter storage technology for energy storage and aggregation capabilities.
Capacity generation
The state has increased its generation capacity over the years, with an emphasis on the upstate. This is partly due the state's electricity being produced in less populated areas. Also, because of gridlock during peak demand, power lines that carry it downstate can also become clogged. In recent years, the State has added 11,846MW of electricity, with a large part of it coming from renewables.
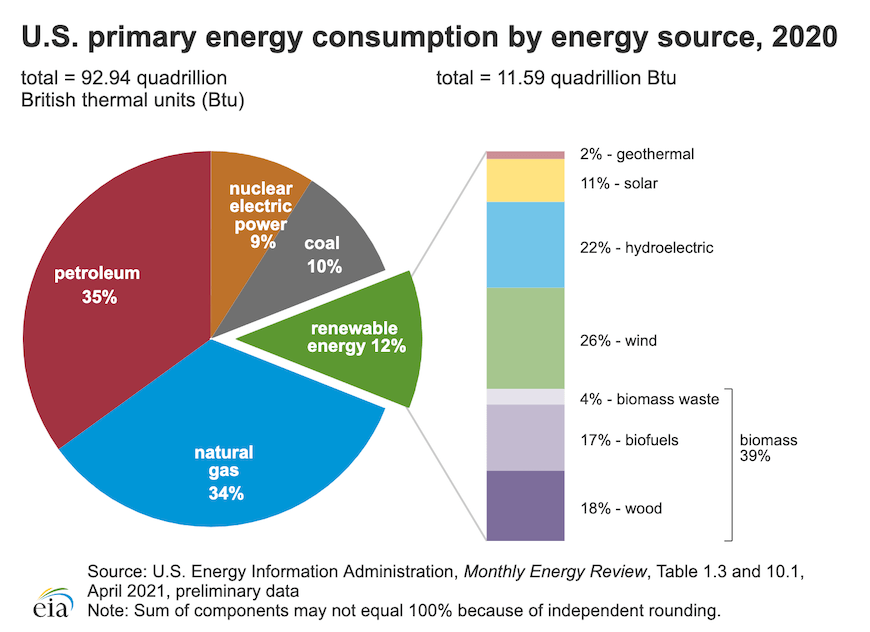
Renewable energy credits
New York state announced plans for expanding its Renewable Energy Credits (RECs), program that helps power plants produce renewable energy. This will help New York achieve its goal to produce 70% renewable energy by 2030. It also helps the state reach its 2040 Zero Emission Target. It will also promote existing renewable energy sources, improve air quality and protect the environment.