
The market for global solar power equipment can be segmented based on equipment, application, or region. Due to increasing awareness among consumers about the advantages of renewable energy, the Asia-Pacific region should lead the market for solar power devices over the forecast period. The Middle East, Africa and Asia-Pacific markets will closely follow.
Energy
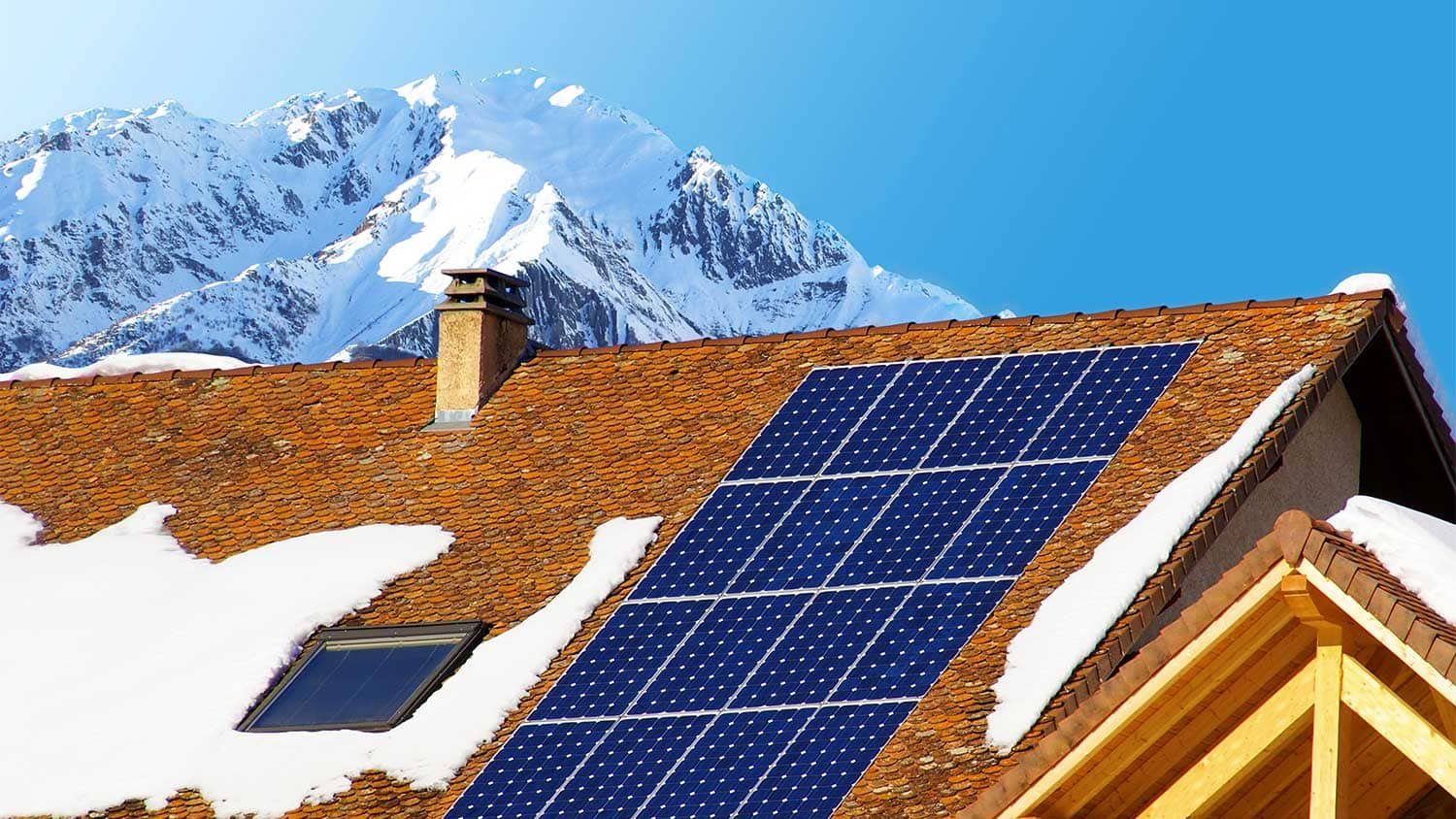
The benefits of using solar energy to generate your own power are numerous. The first benefit is that solar panels do not emit any pollution and don't burn fossil fuels. Solar equipment is heavy so it must be mounted on a strong roof. It must also be exposed to the sun to produce energy. The efficiency of solar power is also affected by the climate and cloud cover. It is crucial to get to know the area where solar energy can be used before making a decision.
Photovoltaic effects are the foundation of the technology behind solar equipment. This effect was discovered by Edmond Becquerel (1839). The semiconductor is able to convert sunlight into electrical current and cause this effect.
Cost
There are many factors that can affect the cost of installing solar equipment. The type of system and size of the system as well as the number of panels will affect the costs. The cost of solar equipment has fallen significantly in recent years. A 4-kW system can cost anywhere from $10,000 to $20,000 or less depending on incentives and credits. Depending upon the type of solar panels you choose, the cost per unit of distributed energy capacity is between $2.50-5. Ask qualified installers for bids on the costs.

The solar inverter costs approximately $0.21/W or eight percent of the total price of solar equipment. Since 2013, solar inverter costs have dropped by 50 percent. This is partially due to higher production and technological improvements.
Efficiency
Solar equipment's efficiency is determined by how efficiently it captures energy and converts it into usable electricity. There are many types of solar equipment that capture energy in different ways. One of the most common types of solar equipment is the photovoltaic panel. This type can convert up to 8% of sunlight into usable energy. Today, silicon solar panels have an efficiency of about 22 percent. The efficiency of silicon solar panels can be increased by using a new crystalline material called Perovskite.
Efficiency of solar equipment is a vital consideration for anyone considering a solar installation. The more energy-efficient solar panel, the lower the overall cost of the system will be. Solar panels with higher efficiency will pay for themselves faster. Some panels are even more efficient than others and will pay off their upfront costs within two years.
Interconnection with Grid
The cost of interconnection to the grid will depend on several factors. They include the size of project, labor costs, and utility's "need" to connect. It is therefore difficult to predict the cost of interconnection. It's important to understand that utilities want to streamline the process for solar project developers.
Before you submit a request, ensure you have read the interconnection process. It generally takes a month or less. The utility will verify that the solar power system meets the standards in your area and that it is safe. If any information is missing, the utility will request that the application be updated or resubmitted. Once the application has been approved, you will be granted permission to use the system.
Supply chain
The supply chain for solar equipments is currently strained. The current supply chain for solar equipments is facing inflationary pressures as well as supply constraints. This situation has resulted in delayed projects and cancellations. This has created a challenging environment for solar developers. The industry should be able fulfill its requirements within the next few years.
China leads the market for solar equipments production and consumption. It accounts for one in every seven solar panels made globally, according to a report published by the IEA. The IEA's report warns governments about China's monopoly on the solar supply chain, and offers suggestions for ways to increase domestic production. It identifies the cost as the major deterrent to foreign countries entering the supply chains. China's manufacturing cost is as low as 20% compared to those in the United States, Europe and India.